Volume 1, Issue 2 (12-2017)
JCES 2017, 1(2): 42-51 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Farooghi F. Influence of axle load on hot-mix asphalt lifetime using elastic method. JCES 2017; 1 (2) :42-51
URL: http://journals.lu.ac.ir/jces/article-1-36-en.html
URL: http://journals.lu.ac.ir/jces/article-1-36-en.html
Assistant professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Kurdistan, Iran
Abstract: (2264 Views)
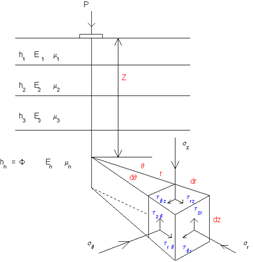
In these studies, the effect of the load types on the stress and the deformation created in the hot-mix asphalt and its lifetime in different qualitative conditions of the surface contact of the layers has been investigated. For this purpose, we have used a set of rules in Iran and France codes. In Iran, the weight of the single-axle load 80 kN and in the French Code the weigh of the dual-axle load is 130 kN. Linear elastic method has been used in structural analysis and fatigue failure and rutting failure has been used to investigate the lifetime of structure. In these studies, the effect of the layer thickness and the two types of contact surface quality (adherence and Non-adherence) are considered. One of the most important results of this study is the significant increase in the vertical strain of the subbase course and horizontal strain of the base course due to single axel load compared to the dual axel load. Inappropriate quality of the layers has increased about 50% of the settlement in the pavement. Also, the effect of single axle load increased about 45% of structural settlement and decreasing of the base and surface courses thicknesse has increased about 30% seattlement in the pavement structure.
Review Paper: Research |
Subject:
Special
Received: 2017/10/18 | Accepted: 2017/12/11 | Published: 2017/12/13
Received: 2017/10/18 | Accepted: 2017/12/11 | Published: 2017/12/13
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |